Table of Contents
Empathy Map is an important part of human-centric design. What is going on in users’ heads is the focal point of user experience (UX) design. It is important to understand the user, thought process, and understand user needs. To connect with users, it is important to empathize with users. That’s when empathy mapping comes in place to understand user frustration, hear their voices and feel their struggle.
Empathy mapping is becoming a crucial source of information in delivering UI/UX design services.
Very often UX designers face conflicting situations between stakeholders and forget about the target audience. Empathy mapping is about getting in users’ shoes during their interaction with a product or application.
What is Empathy Map
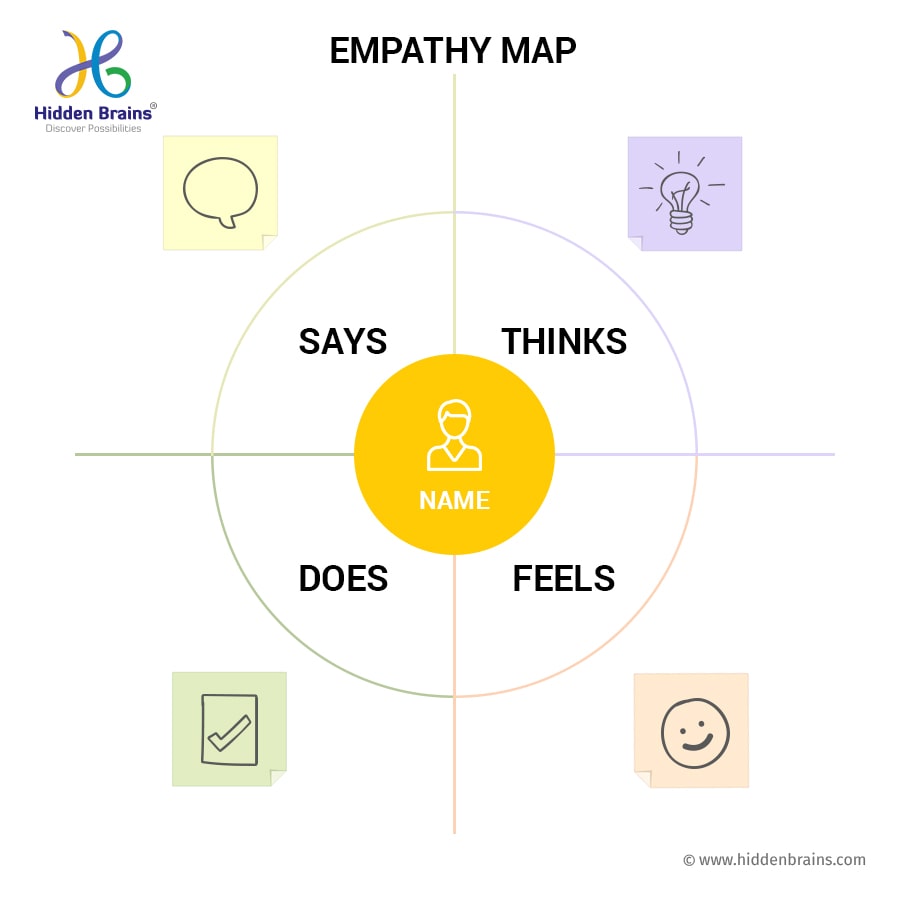
An empathy map is easy-to-digest visual deciphering a user’s behaviors and attitudes. It is an effective tool and a highly focused way to understand users. Empathy map allows understanding user groups’ emotions, amalgamating observations, and gauging actionable insights
Also Read: Stages of Design Thinking and How it Works
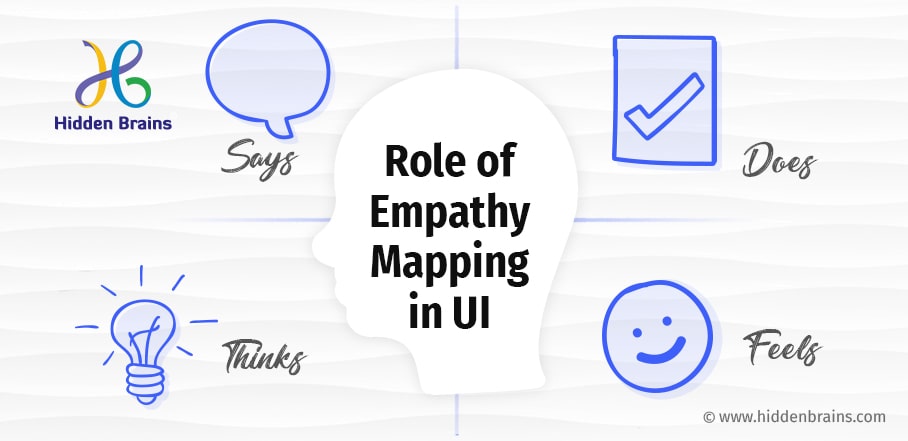
Typical empathy map includes four quadrants:
Say – This section records what users say about the product. It mainly contains real quotes from users during interviews or testing sessions.
- “I want something durable.”
- “I don’t like the texture”
- “I don’t see any value for money”
Thinks – This section is about finding out what the user is thinking about when interacting with a product? It outlines the user’s thoughts and what matters the most to the user. However, users may not vocalize what they think. It may show their reluctance to share something.
- “Do they think I don’t understand?”
- “Am I dumb to buy that?”
Does – This quadrant focuses on user actions, any typical behavior noticed on the app or website, as well as remarks related to site/applications.
- Refreshes page several times
- Check out as a guest
- Mistakenly visit settings
- Cant’ remember the password
Feels – This section contains information about the user’s emotional state and how user emotions fluctuate throughout the journey.
Importance of Empathy Mapping in UI/UX Design Services
During the early stage of designing, empathy mapping helps know the user’s world and provides a pragmatic approach to creating solutions. This approach applies to a webpage design, app prototype, or new service offering.
The maps can also be used throughout the design process and revised as new data becomes available. A map with more questions than answers effectively indicates more user research needs to be done.
The benefits include:
- User understanding
- A visual depiction of information
- Key actionable insights
- Fast and inexpensive
- Customization for information and goals
- A common understanding among teams
How to Build an Empathy Map
Scope and goals
Identify User Persona: Will you map a persona or user? If you map multiple personas, there is a need to build an empathy map for each persona.
Purpose for empathy mapping: Is it to sync up the team on your user or analyze an interview? If so, set a clear scope to ensure you have time to map multiple user interviews.
Create a Script
Think through the questions, decide who you want to ask questions, what you want to know, why they answer and why do they feel that way.
Gather materials
Create a system that works for empathy mapping. If you are working for a large team make information sharing easier.
Collect research
Narrow down on qualitative methods such as user interviews, surveys, field visits, and more.
Generate notes for each quadrant
Digest information that aligns and the map he information on to one of the four quadrants
Cluster and synthesize
Clustering improves discussion and reaches a shared understanding of your user by all team members. Classify themes and understand the gaps.
Refine and Plan
Based on an empathy map, refine and digitize the output accordingly to make UX decisions.
Finally
Quick tips to create an Empathy Map
Don’t get fixated with quadrants
It is important not to get obsessed with putting things in the “right” quadrant. Remember, the end goal is to connect with the audience and not to classify information.
Get selective about the project goal.
It is equally important to know about audience emotions that will have a direct implication for your work.
Adapt the map
Change the categories based on your work, persona, or data.